All summer caring for the garden beds, each of us certainly wants to see the result of their efforts, gathering in the autumn harvest. But there is an old saying: «Smart cultivates the crop, and wise land». Therefore, to achieve the desired result and to harvest with a fragrant and juicy fruit, in the cultivation of garden beds you should not forget about crop rotation of vegetable crops. This effective natural system of gardening not only helps to maintain soil fertility, but also significantly reduce the number of diseases and pests affecting vegetable crops.
The contents
What tasks does the rotation?
For intensive development and growth of plants requires the predominance of certain macronutrients, because vegetable crops have different ability to absorb these elements. For example: the root vegetables (potatoes, carrots, beets) in a large enough quantity of the required phosphorus, and leaf crops (cabbage, lettuce) – nitrogen. And if the roots due to well developed root system to supply able to use the lower soil layers, rich in potassium and phosphorus, the roots of the leafy greens are able to get the necessary for the development of minerals only of the upper layers of soil…

The main task, which solves the crop rotation in the garden – a uniform distribution in the soil of nutrients
Landing on the designated area from year to year one type of vegetable crops leads to a significant depletion of the soil and a noticeable shortage of a particular element.

Only well-organized rotation on the plot gives the opportunity to use all the advantages of a fertile soil
The vegetables belonging to the same family, in the ground begin to accumulate the pathogens and pests that affect this family. In the case of planting the same crops that are growing this summer on a separate bed, there is always a chance to obtain the fruit affected by disease. If the landing site crops annually alternate, not finding suitable food, disease-causing microorganisms simply die. The best option, when members of the same family return to the old landing place not earlier than 3-4 season.
In addition, grouping plants in the garden, taking into account their needs much easier to care for the plantings. Thanks to well-thought-out crop rotation in the country can even compete successfully with weeds. Even experienced gardeners have long noted that the culture, build a small vegetative mass (parsley, carrot) is not able to withstand the growth of weeds as plants with a growing leaf area (pumpkin, zucchini, potatoes).
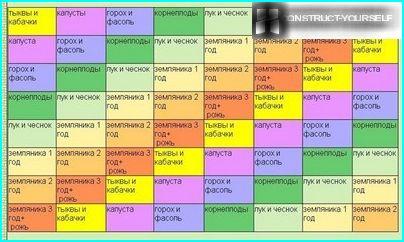
The scheme of planting, where the horizontal rows indicate the year of planting (first, second…), and the vertical bars on the plots of crops

Thanks to the alternation of beds to create the most favorable conditions for the growth and development of vegetable beds
A variety of variations of the rotation system
Over many years of practice, many growers, especially given the development of the plant root system and assimilation of nutrients from the soil, learned how to optimally alternate the garden vegetables. Based on the simplest scheme of crop rotation is the principle that no annual crop should not grow at the same place two seasons in a row. More complex combinations of crop rotations include development of the optimal change of plants within the same plot for several years to come.
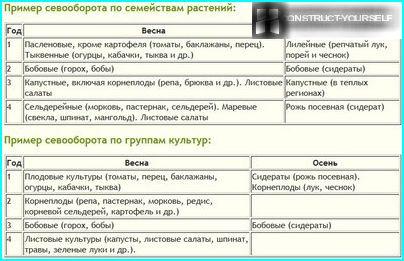
When mapping experts mainly focus on two parameters: the alternation of families and change of crops (root, fruit, leaf group)
Combined with large plants such as cabbage, zucchini and tomatoes, vegetables of small size: onion, carrot, radish. As intermediate landings between the main harvest, you can use of early-ripening crops: cabbage, radish, lettuce, spinach.
If the mapping of the rotation to be based on the compatibility of plants, the best options can be considered:
- predecessors cabbage — tomatoes, potatoes, peas, lettuce and onions;
- carrots, parsnips, parsley and celery — after the potatoes, beets or cabbage;
- early potato and tomato after onions, cucumber, beans, and cabbage;
- squash, pumpkin and zucchini – after root vegetables, onions and cabbage;
- radish, turnips and radishes, after potatoes, tomato, cucumber;
- cucumber – after the cabbage, beans, tomato and potato;
- lettuce, spinach and dill – after the cucumber, tomato, potato and cabbage;
- onion after potato, cabbage, cucumber.
In the fight against pests of vegetable crops (a leaf, tongs, scoops) are herbs. Live well with vegetable crops:
- Broccoli salad with lettuce and parsley;
- Tomatoes with savory, spinach and watercress;
- Cucumbers with dill;
- Radishes and carrots with parsley and chives;
- Strawberries with parsley.
Well-chosen vegetables are able to provide each other a beneficial effect. And a good combination of plantings of vegetable crops with herbs benefits and creates a harmony of beauty.

Not recommended to plant next to the culture «relatives», which often affects common diseases. Planted close to tomatoes and potatoes can suffer from blight
How to make your rotation pattern?
Deciding to make a rotation pattern in the suburban area, you should first make a plan of the garden, where to locate your vegetable and fruit crops.

The plan should consider not only soil composition of the site, but the degree of illumination of the beds of the garden at different times of the day
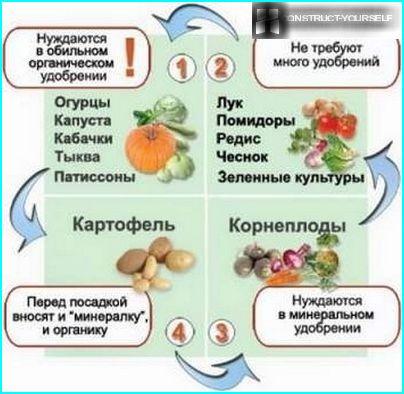
Feature crops is that they have different nutritional needs. Depending on the degree of consumption of the soil trace elements and nutrients in vegetable crops can be divided into 3 groups:
- Plants with a weak demand. Among undemanding to soil structure crops include: onions, lettuce, herbs, radish, peas, Bush beans.
- Plants with an average severity of nutrients. These include: tomatoes and cucumbers, beets and radish, melon, eggplant, and leek, spinach, kohlrabi and curly beans.
- Plants with a high need. These include: zucchini, celery, potatoes, pumpkin, asparagus, rhubarb, cabbage, spinach.
Mapping of crop rotation, drafted the plan should be divided into 3 or 4 parts, following which it will be possible to follow, that each culture has returned to its former place of landing only on the third or fourth year.
First the most fertile part of the garden provide a landing «voracious» crops (cabbage, cucumbers, zucchini). The second part of the plot is used for planting eggplant, peppers, tomatoes, which are less demanding of soil fertility, or radishes, onions or herbs. The third part is withdrawn for crops, which are able to give a good crop on relatively poor soil. Here are planted: turnips, carrots, beets, and parsley. In the last quarter of the garden planted potatoes, locally introducing into each well organic fertilizers (rotted manure or compost with ashes).
After harvest, the vacant beds, it is desirable to plant plants green manures that are better than any fertilizer will improve fertility of the soil
The next season the plants that grew in the first section, uniformly moving in a circle, «move» on the fourth, from second to first, from third to second, etc.
When drawing up schemes of crop rotation should also take into account the structural features of the root system of plants and their depth of penetration into the soil. Due to this, the nutrients will be evenly used from different soil layers. For example: cucumbers, onions and cabbage can eat with topsoil, the roots of the tomato penetrates to a depth slightly less than a meter, and the corn is up to two meters.
Knowing the peculiarities of each culture and given a good combination between them, not only to achieve a rich harvest, but also to protect plants from many diseases.